백준 14500 - 테트로미노 [C/C++] BFS 알고리즘
14500번: 테트로미노
폴리오미노란 크기가 1×1인 정사각형을 여러 개 이어서 붙인 도형이며, 다음과 같은 조건을 만족해야 한다. 정사각형은 서로 겹치면 안 된다. 도형은 모두 연결되어 있어야 한다. 정사각형의 변
www.acmicpc.net
문제 설명은 다음과 같다.
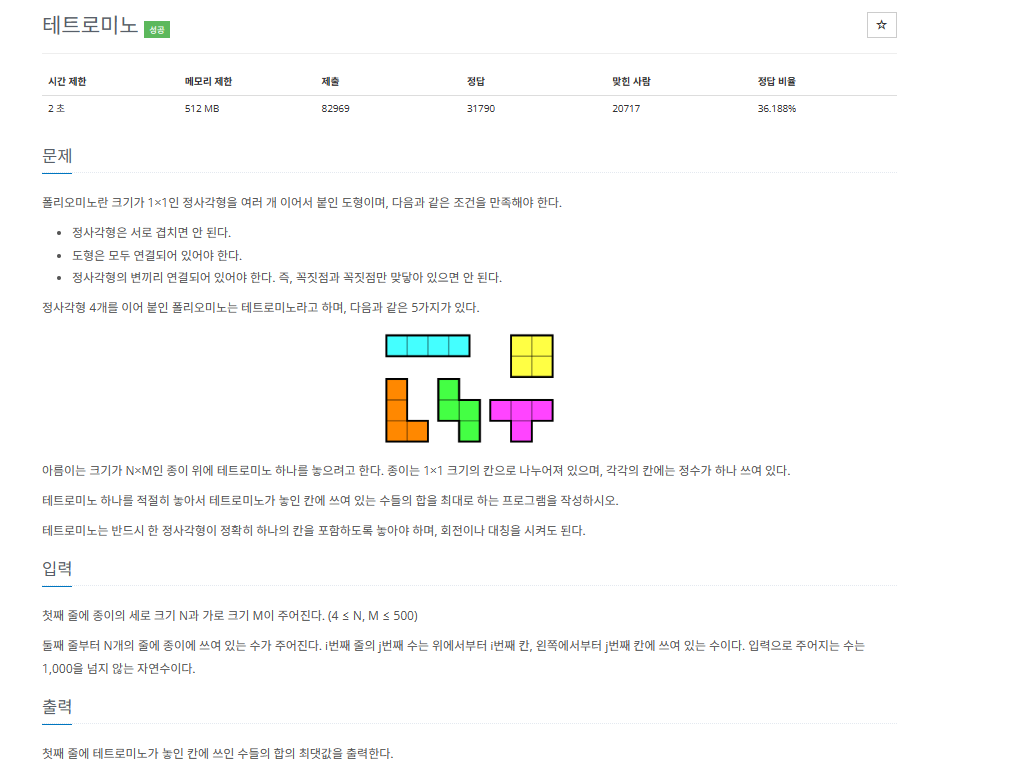
생각보다 조금 귀찮은 문제였다.
DFS로도 풀 수 있긴 한데, 본인은 BFS가 더 편하기도 하고, 이걸로도 풀릴 것 같아서 BFS로 풀었다.
우선 4개의 블록으로 만들 수 있는 모양 중 ㅜ ㅗ ㅓ ㅏ 블록의 모양 같은 경우는, BFS로 풀어도 의미가 없는게, 한쪽으로 갔다가 돌아오는 작업이 필요한데, 이는 BFS로는 구현이 상당히 귀찮아질 뿐더러 힘들다.
그래서 저 4개의 블록같은 경우는 그냥 if로 분기 처리해주어서 따로 빼주었다. (어쩔 수 없음)
나머지 블록은 그냥 BFS로 밀어도 가능하다고 생각해서, 평범하게 visited 확인해주면서 BFS로 밀었다.
우선 코드를 보자.
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
#define fastcpp ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0)
using namespace std;
int height, width;
int map[500][500];
bool visited[500][500];
int dx[4] = {0,1,0,-1};
int dy[4] = {1,0,-1,0};
int bfs(int start, int high) {
queue<pair<pair<int,int>,pair<int,int>>> q;
q.push({{start,high},{map[high][start],1}});
int sum = 0;
int maxV = 0;
if (start-1 >= 0 && start+1 < width && high+1 < height){
int dap = map[high][start] + map[high+1][start] + map[high][start+1] + map[high][start-1];
maxV = max(maxV, dap);
}
if (start-1 >= 0 && start+1 < width && high-1 >= 0) {
int dap = map[high][start] + map[high-1][start] + map[high][start+1] + map[high][start-1];
maxV = max(maxV, dap);
}
if (high+2 < height && start + 1 < width){
int dap = map[high][start] + map[high+1][start] + map[high+2][start] + map[high+1][start+1];
maxV = max(maxV, dap);
}
if (high+2 < height && start - 1 >= 0) {
int dap = map[high][start] + map[high+1][start] + map[high+2][start] + map[high+1][start-1];
maxV = max(maxV, dap);
}
if (high + 1 < height && start + 1 < width){
int dap = map[high][start] + map[high+1][start] + map[high+1][start+1] + map[high][start+1];
maxV = max(maxV, dap);
}
while(!q.empty()){
int x = q.front().first.first;
int y = q.front().first.second;
int sum = q.front().second.first;
int cnt = q.front().second.second;
visited[y][x] = true;
q.pop();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int next_x = x+dx[i];
int next_y = y+dy[i];
if (next_x < 0 || next_y < 0 || next_x >= width || next_y >= height) continue;
if (visited[next_y][next_x]) continue;
if (cnt>=4) {
maxV = max(maxV, sum);
continue;
}
q.push({{next_x,next_y},{sum+map[next_y][next_x],cnt+1}});
}
}
return maxV;
}
int main() {
fastcpp;
cin >> height >> width;
for (int i=0;i<height;i++){
for (int j=0;j<width;j++){
cin >> map[i][j];
}
}
int maxV = 0;
for (int i=0;i<height;i++){
for (int j=0;j<width;j++){
memset(visited, false, sizeof(visited));
int a = bfs(j,i);
maxV = max(maxV, a);
}
}
cout << maxV;
return 0;
}
코드가 좀 어지러울 수 있지만, 그래도 100줄도 안되는 짧은 코드이다.
우선 BFS의 근간에 따라서, 큐에 무언가를 쌓으면서 pop 시키면서, 조건을 만족하나? 아님말고. 식의 코드를 평범하게 짰다.
- 여기서 조건은 우선 map 바깥으로 넘어갔는지 아닌지
- 이미 방문했는지
- 블록의 수가 4가 되었는지
큐에 들어가는 것은 pair 두 개 인데, 첫 번째 pair에는 좌표 두 개가 들어가고, 두 번째 pair에는 현재까지 더한 값과 몇 개의 블록이 쌓였는지가 들어가 있다.
이 때, 이미 방문했는지를 체크하고, 방문했다면 넘어가도 된다.
- 이게 나중에 조금 문제였는데, 나머지 블록은 다 통과했는데, 정사각형 모양을 체크하지 못하는 경우가 있었다.
- 끝내 고민하다가... 그냥 if로 따로 떼줬다 허허(?)
블록의 수가 4가 되었다면, 지금까지 다 더한 값과 max 값을 비교해서 max값을 업데이트한다.